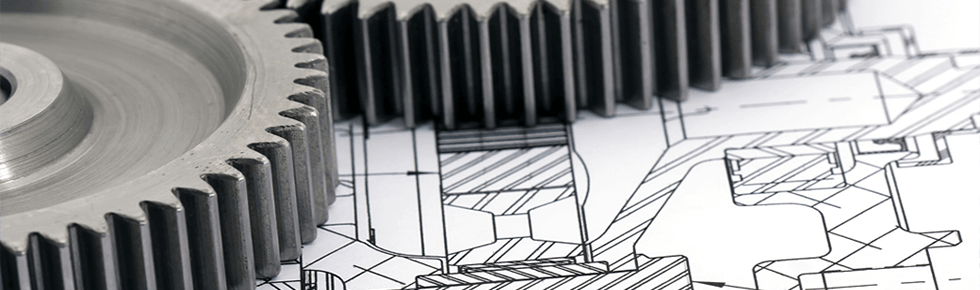
Application machinery
In machinery 3D printers are used at all stages of product development: starting with creating a conceptual model and ending with production planning, which significantly speeds up and simplifies the development process for design engineers. 3D printing is primarily used to visualize objects of different complexity. It can be both the whole model of cars, and various mechanisms. Using 3D modeling, you can create a scaled three-dimensional image of any part of the car, ranging from cylinders in the engine and ending with the dashboard, but this model will not give a complete picture without a real prototype in your hands.
Rapid prototyping is the direction where 3D printing is most used in machinery, starting with the first ideas and ending with the prototype of the finished product. The incredible speed of production, high accuracy and variety of materials allow in the shortest possible time and with the highest quality to submit the first samples for testing.

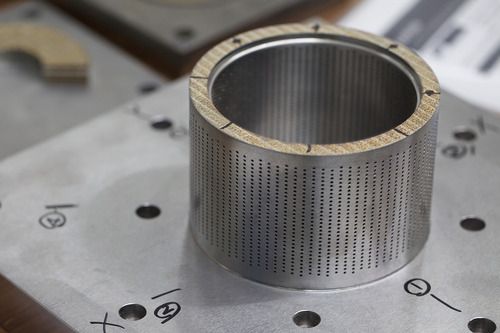
3D printing technology Stratasys FDM (Fused deposition modeling) has allowed engineers to take a new level in the use of 3D printers in machinery. Functional prototypes can be made on their equipment from different engineering and high-tech plastics, as a result, products can be machined, drilled and mechanically affected. The moisture resistance and heat resistance of the prototypes during the tests will correspond to the characteristics of the final product. Machine-building enterprises use printed parts to inspect the entire product mix and to ensure that every workplace has all the necessary tools to achieve the highest possible production efficiency. Making a variety of tooling with real industrial plastics allows speeding up the release of finished products, and the burned tooling for casting - to get a molded product with high accuracy in the shortest lines.
In recent years, more and more companies began to resort to 3D printing with metals, which in turn made it possible to produce finished products of complex shape, which cannot be repeated using traditional methods. Getting finished products with such equipment is measured in a few days, maybe even hours, and the manufacture of spare parts is a quickly solvable task. The prospect of using 3D printers for machinery is economically obvious, since these devices significantly speed up the process of developing new products, significantly reduce the risks of design errors, reduce the cost of obtaining the layout, and are now at their prices are available to most businesses.
 English
English  Українська
Українська 